Interjections and Their Types in Detail
Interjections are an essential part of speech used to express strong emotions, sudden reactions, or spontaneous feelings in spoken and written communication. They often stand alone and are not grammatically related to other parts of a sentence. Interjections can convey emotions such as happiness, surprise, frustration, excitement, or pain.
What is an Interjection?
An interjection is a word or phrase that expresses sudden emotions or reactions. It usually appears at the beginning of a sentence and is followed by an exclamation mark, comma, or period depending on the intensity of the emotion.
Examples:
• “Wow! That’s amazing!”
• “Oh, I didn’t expect that.”
• “Oops! I dropped the glass.”
Types of Interjections
Interjections can be classified based on the emotions they express and the context in which they are used. The main types of interjections include:
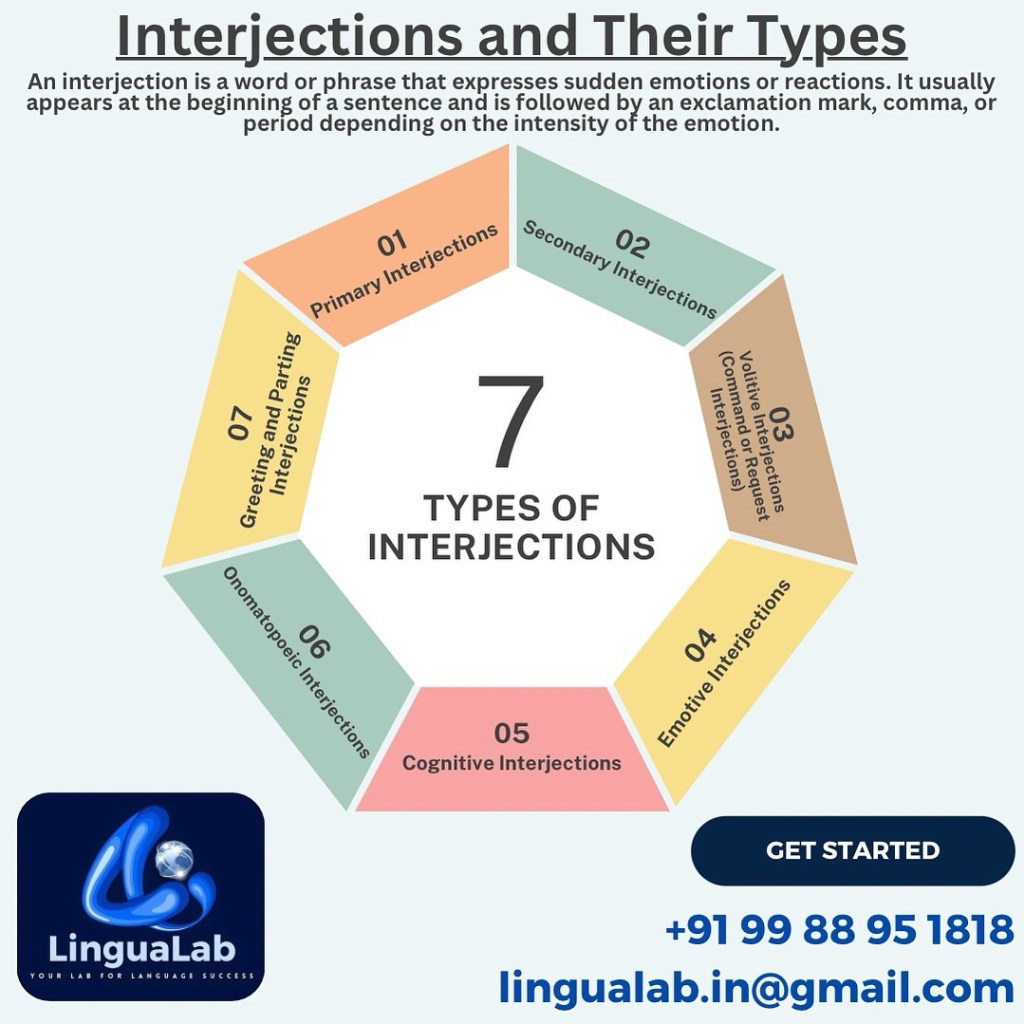
1. Primary Interjections
These are standalone words that do not have any specific meaning but are used to express emotions directly.
Examples:
• Happiness: Wow! Hurrah! Yay!
• Surprise: Oh! Ah! Eh!
• Pain: Ouch! Aah!
• Disgust: Ugh! Ew!
• Approval: Bravo! Well done!
2. Secondary Interjections
These are words or phrases that are primarily used in other grammatical roles but can function as interjections when expressing emotions.
Examples:
• “Oh God! I can’t believe this happened.” (God – noun)
• “Indeed, you were right!” (Indeed – adverb)
• “Goodness! What a beautiful dress!” (Goodness – noun)
3. Volitive Interjections (Command or Request Interjections)
These interjections are used to give orders, commands, or requests in a forceful or polite manner.
Examples:
• “Shh! Keep quiet.”
• “Hush! Don’t wake the baby.”
• “Listen! I have something important to say.”
4. Emotive Interjections
These express strong emotions such as joy, sorrow, frustration, or excitement.
Examples:
• “Alas! We lost the match.” (Sorrow)
• “Yippee! We won the lottery.” (Excitement)
• “Darn! I missed the train.” (Frustration)
5. Cognitive Interjections
These interjections convey thoughts, realizations, or hesitation and are often used in informal speech.
Examples:
• “Hmm, let me think about it.” (Hesitation)
• “Aha! I knew you were lying.” (Realization)
• “Eh? What did you say?” (Confusion)
6. Onomatopoeic Interjections
These interjections imitate sounds associated with objects, animals, or actions.
Examples:
• “Bang! The door slammed shut.” (Sound of an impact)
• “Moo! The cow is in the field.” (Animal sound)
• “Whoosh! The wind is blowing fast.” (Nature sound)
7. Greeting and Parting Interjections
These interjections are used to greet or bid farewell to others.
Examples:
• “Hello! How are you?” (Greeting)
• “Bye! See you tomorrow.” (Parting)
• “Hey! Long time no see.” (Casual greeting)
Usage of Interjections in Sentences
Interjections are versatile and can be placed at different positions within a sentence.
Examples:
• At the beginning: “Oops, I forgot my keys!”
• In the middle: “The trip was, wow, absolutely amazing!”
• At the end: “You did a great job, bravo!”
Punctuation with Interjections
The punctuation used with interjections depends on the intensity of emotion:
• Exclamation Mark (!): Used for strong emotions.
“Yay! We are going on vacation!”
• Comma (,): Used for mild emotions or pauses.
“Oh, I see what you mean.”
• Period (.): Used for subtle interjections.
“Well. That’s unexpected.”
Interjections play a crucial role in adding emotion, spontaneity, and emphasis to communication. Whether expressing joy, surprise, sadness, or hesitation, they bring authenticity and liveliness to conversations and writing. Mastering the use of interjections can help in making communication more natural and expressive.








Leave a comment