Prepositions: A Detailed Overview
A preposition is a word that connects nouns, pronouns, or phrases to other words within a sentence. It typically indicates relationships in terms of time, place, direction, cause, manner, and possession.
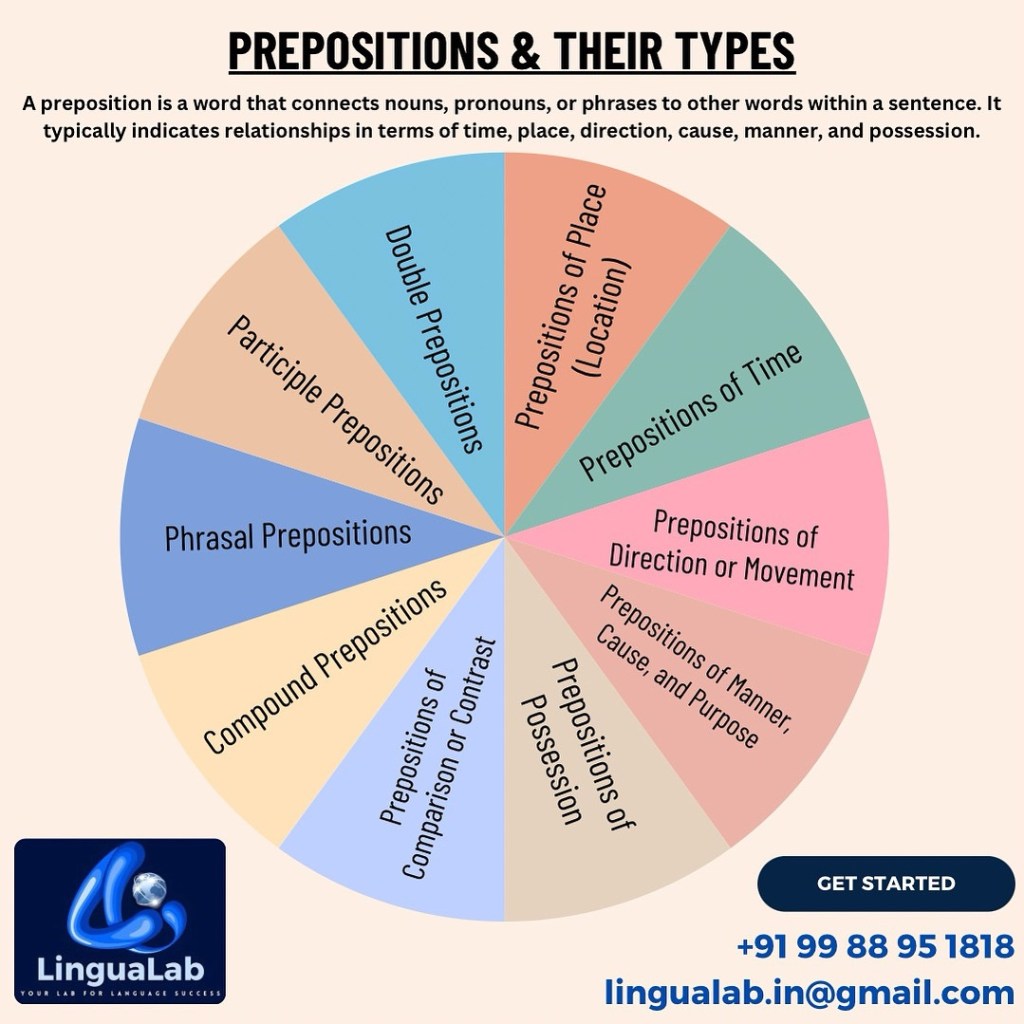
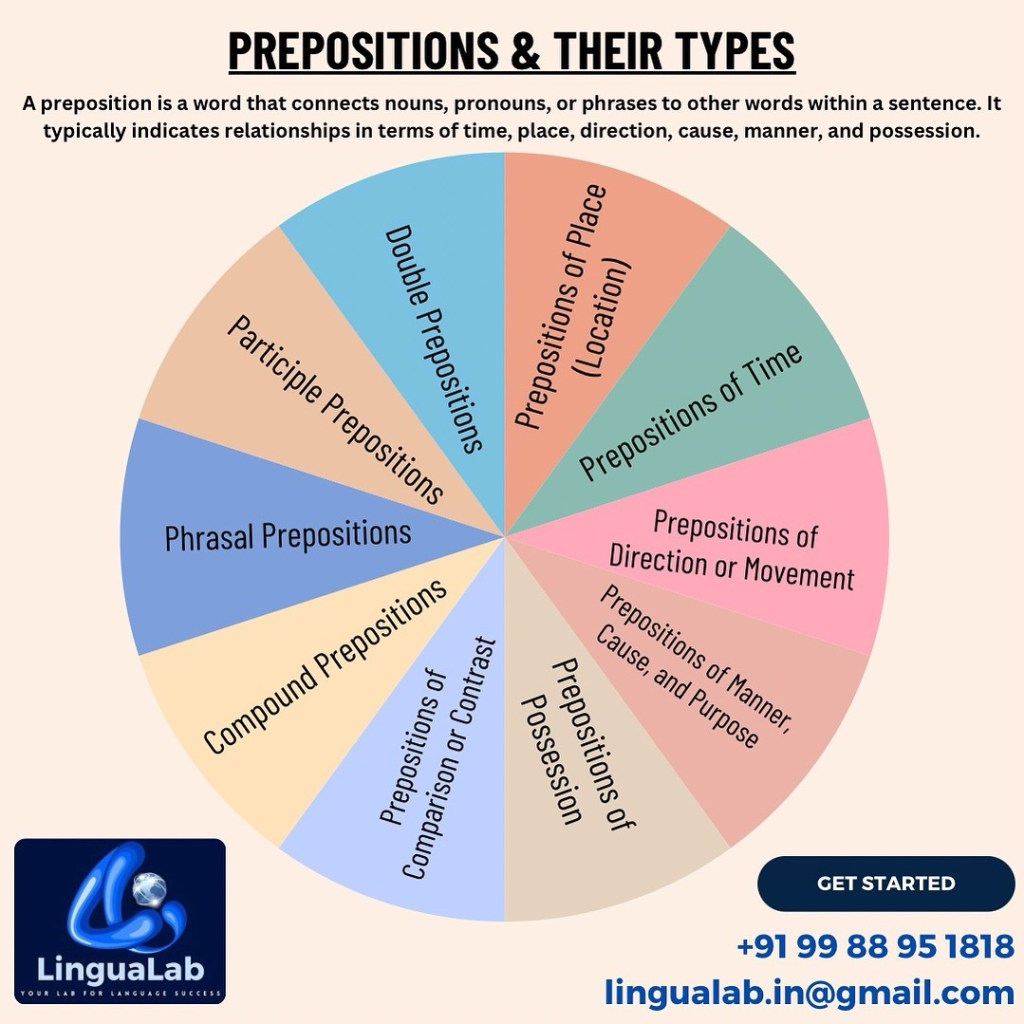
Types of Prepositions
Prepositions can be categorized into several types based on their usage and function.
1. Prepositions of Place (Location)
These prepositions show the position or location of an object in relation to another object.
Common Prepositions:
• In – The book is in the bag.
• On – The phone is on the table.
• At – She is at the door.
• Under – The shoes are under the bed.
• Between – The park is between the school and the mall.
• Behind – The car is behind the building.
• Next to – The shop is next to the bakery.
2. Prepositions of Time
These prepositions indicate when something happens.
Common Prepositions:
• In – I was born in July.
• On – The meeting is on Monday.
• At – We eat dinner at 8 PM.
• By – I will finish the work by tomorrow.
• Since – He has been working here since 2010.
• For – They stayed in Paris for a week.
• Until – Wait here until 5 PM.
3. Prepositions of Direction or Movement
These prepositions show movement from one place to another.
Common Prepositions:
• To – We are going to the market.
• Into – He walked into the room.
• Onto – She jumped onto the bed.
• Out of – He came out of the house.
• From – They moved from Delhi to Mumbai.
• Towards – She walked towards the station.
4. Prepositions of Manner, Cause, and Purpose
These prepositions describe how, why, or for what purpose something happens.
Common Prepositions:
• By – She traveled by car.
• With – He cut the paper with scissors.
• Because of – The game was canceled because of the rain.
• Due to – The flight was delayed due to fog.
• For – This gift is for you.
5. Prepositions of Possession
These prepositions indicate ownership or relationships.
Common Prepositions:
• Of – The pages of the book are torn.
• With – The girl with the blue dress is my friend.
• To – This belongs to me.
6. Prepositions of Comparison or Contrast
These prepositions compare or contrast things or people.
Common Prepositions:
• Like – He runs like a professional.
• Unlike – Unlike his brother, he is very quiet.
• Than – She is taller than him.
• As – Work as a teacher.
7. Compound Prepositions
These are prepositions formed by combining two or more words.
Examples:
• According to
• Because of
• In front of
• On account of
• In spite of
8. Phrasal Prepositions
These consist of a phrase that functions as a preposition.
Examples:
• In addition to
• In comparison with
• With regard to
• In reference to
9. Participle Prepositions
Prepositions that end in “-ing” and act as links between elements in a sentence.
Examples:
• During
• Following
• Considering
10. Double Prepositions
These prepositions are formed by combining two simple prepositions.
Examples:
• Into
• Onto
• From within
• Up to
• Out of
Rules for Using Prepositions
1. A preposition is always followed by a noun or pronoun (never by a verb).
• Incorrect: She is good in cooking.
• Correct: She is good at cooking.
2. Some prepositions have fixed phrases.
• Interested in, good at, afraid of, etc.
3. Avoid unnecessary prepositions at the end of sentences.
• Incorrect: Where are you going to?
• Correct: Where are you going?
Common Prepositional Errors
• Incorrect: I am waiting since two hours.
• Correct: I have been waiting for two hours.
• Incorrect: She is married with John.
• Correct: She is married to John.
By understanding and using prepositions correctly, you can enhance your communication skills and avoid common grammar mistakes.
#prepositions #place #onlineclasses #time #manner #types #Grammar #EnglishGrammar #OnlineGrammarClasses








Leave a comment